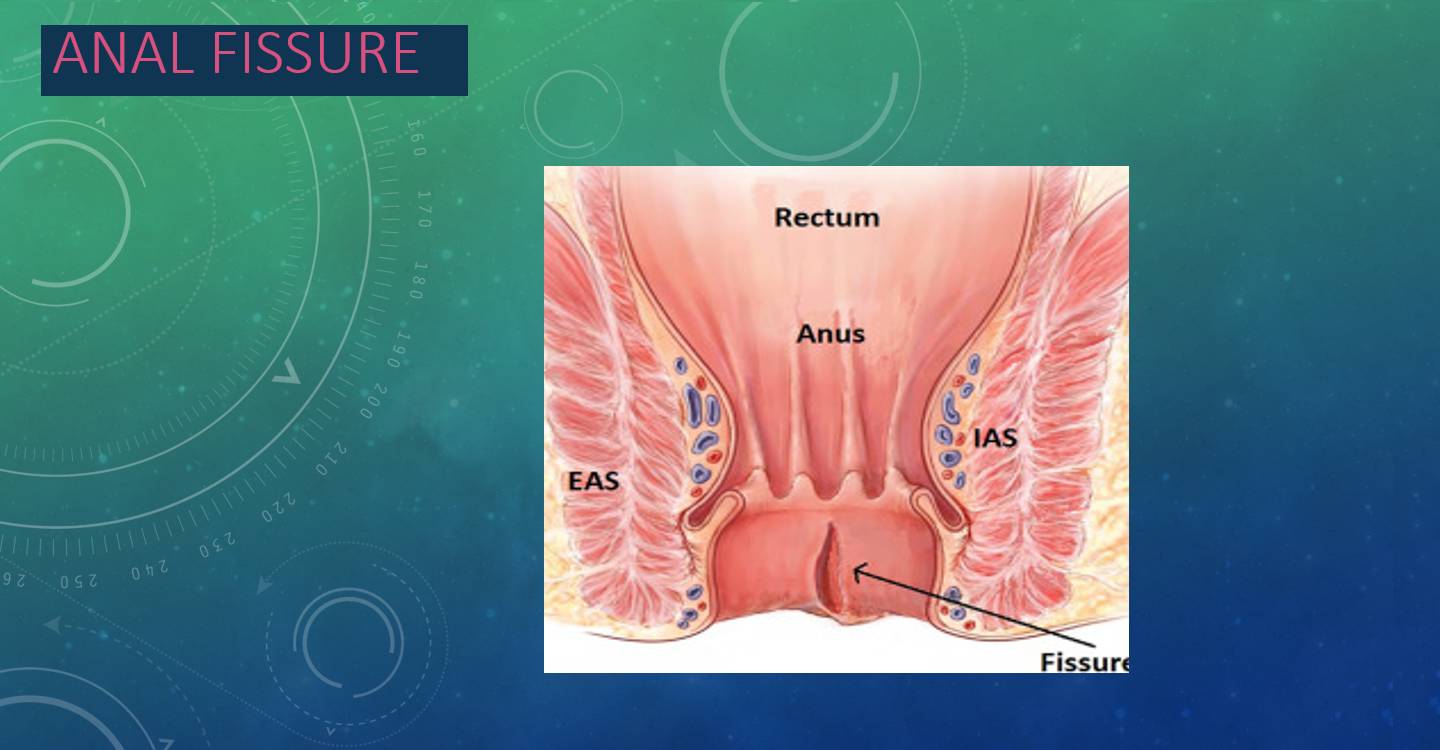
What is anal fissure ?
Anal fissure as name implies is a tear in the lining of the distal most part of anal canal or back passage .
Anal fissure can be acute ( less than 6 weeks duration ) or it can be chronic ( persisting beyond 6 weeks )
What are the Causes of Anal fissure ?
The exact cause remains uncertain.
It typically occurs after the passage of a large, hard stool or anal trauma. Bad dietary habits, low consumption of dietary fibre leading to constipation , is one of the prime cause.
Fissures can also occur in the absence of any trauma or constipation.
Atypical fissures: These Can occur anywhere in the anal canal & tend to be associated with other diseases, including malignancy, Crohn’s disease, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, syphilis, and tuberculosis.
Theories: –
Mechanical Theory: The anorectal angle creates the greatest stress posteriorly. It remains undetermined if Sphincter hypertonicity which is documented by manometry in multiple studies, is the cause of the disease or an effect.
Ischemia Theory: The posterior midline of anoderm is relatively low in vascularity which has been shown by both arteriographic studies and laser Doppler. Hence posterior anal fissure are more common (85% - 90%) than anterior fissures ( 10%- 15%).
CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF ANAL FISSURE
Acute fissures (<6 weeks)
Bright red bleeding with bowel movements. Sharp, burning, tearing anal pain or spasm. Can last for hours after the bowel movement. Physical findings: linear separation of the anoderm, visible with just separation of the buttocks
Chronic fissures (>6 weeks)
Additional physical findings of an external sentinel tag at the external apex, exposed internal sphincter muscle, and a hypertrophied anal papilla at the internal apex
Typical fissures are located in the posterior or anterior midline .They are not associated with other diseases.
Atypical fissures: Can occur anywhere in the anal canal.
TREATMENT OF ACUTE ANAL FISSURES
It has long been recognized that acute fissures can be cured conservatively.
1. Warm water sitz bath with or without addition of Betadine and rock salt. This treatment soothes the pain and relaxes the spasm of the internal sphincter for some time. This should be carried out several times a day and after each bowel movement.
2. Stool softening is essential, as soft and formed stools negotiate the rectum and anal canal in non-traumatic physiologic way. Plenty of oral fluids also help in keeping the stools soft.
3. High-fibre-diet and bulk-forming agents such as Ispaghula; green leafy vegetables and fibrous fruits go a long way in increasing the bulk of stool leading to a smooth and swift act of defecation.
4. Reassurance and encouragement for not resisting the urge for defecation help prevent hard stools. Later the patient could be encouraged to acquire and maintain a regular bowel habit of once or twice a day.
5. Application of local anaesthetic cream or gel may help avoid the torture experienced in passage of stools in the patients with acute fissures. Ointments containing xylocaine, and soothing agents can help in relieving pain. These mixtures are introduced on the finger instead of using as suppositories.
TREATMENT OF CHRONIC OR COMPLICATED FISSURES
The approaches mentioned for treating acute fissures do not prove effective in the chronic variety of fissures. These chronic or complicated fissures are not amicable to the simple conservative line of treatment. A definitive therapy is needed to tackle this stubborn problem.
Treatment of chronic fissures could be operative or non-operative.
Non-operative techniques
1] Injection of Botulin Toxin : Botulin toxin (Botox) is known to cause paresis of the sphincter. This causes sphincter relaxation for about 3 months, a period which is sufficient for healing of a chronic uncomplicated anal fissure. It is well tolerated and can be administered on an outpatient basis. The healing rate reported is about 79%.
2]Calcium Channel Blockers : Both diltiazem and nifedipine cause relaxation of the smooth muscle of the internal anal sphincter. Relaxation of sphincter eases away the pain . Additional vasodilatation effect helps in healing of the fissure.
Fissure healing rate is up to 68%. Headache during treatment is a major drawback of the above topical medications.
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ANAL FISSURES
Surgery has a very important role to play in management of Anal fissures which fail to respond to conservative line of treatments.
LORD’S anal dilatation, once popular technique where a simple stretching of anal sphincter muscles was performed under general anaesthesia, has become obsolete due to complication of anal incontinence.
LATERAL INTERNAL SPHINCTEROTOMY :
Division of the internal anal sphincter either up to the length of anal fissure or up to the dentate line , using surgical blade or a cautery has been proved very effective in pain relief as well as healing of the fissure.
Properly done sphincterotomy by experienced surgeon, does not lead to incontinence.
The associated anal skin tags and hypertrophied anal papilla are removed at the same time.
Internal sphincterotomy is offered only to patients having a high anal sphincter tone.
In patients who present with Anal fissure associated with Hypotonic anal sphincter, ANORECTAL advancement flap is offered as a means of surgical treatment. Success rate is up to 98% without any complication of incontinence.
RECENT ADVANCES IN TREATING ANAL FISSURE :
Diode LASER is being used to carry out the lateral sphincterotomy.
LASER treatment is minimally invasive, painless & bloodless with ultrashort recovery period.
LASER SPHINCTEROTOMY is nowadays the treatment of choice in experienced hands whenever available.