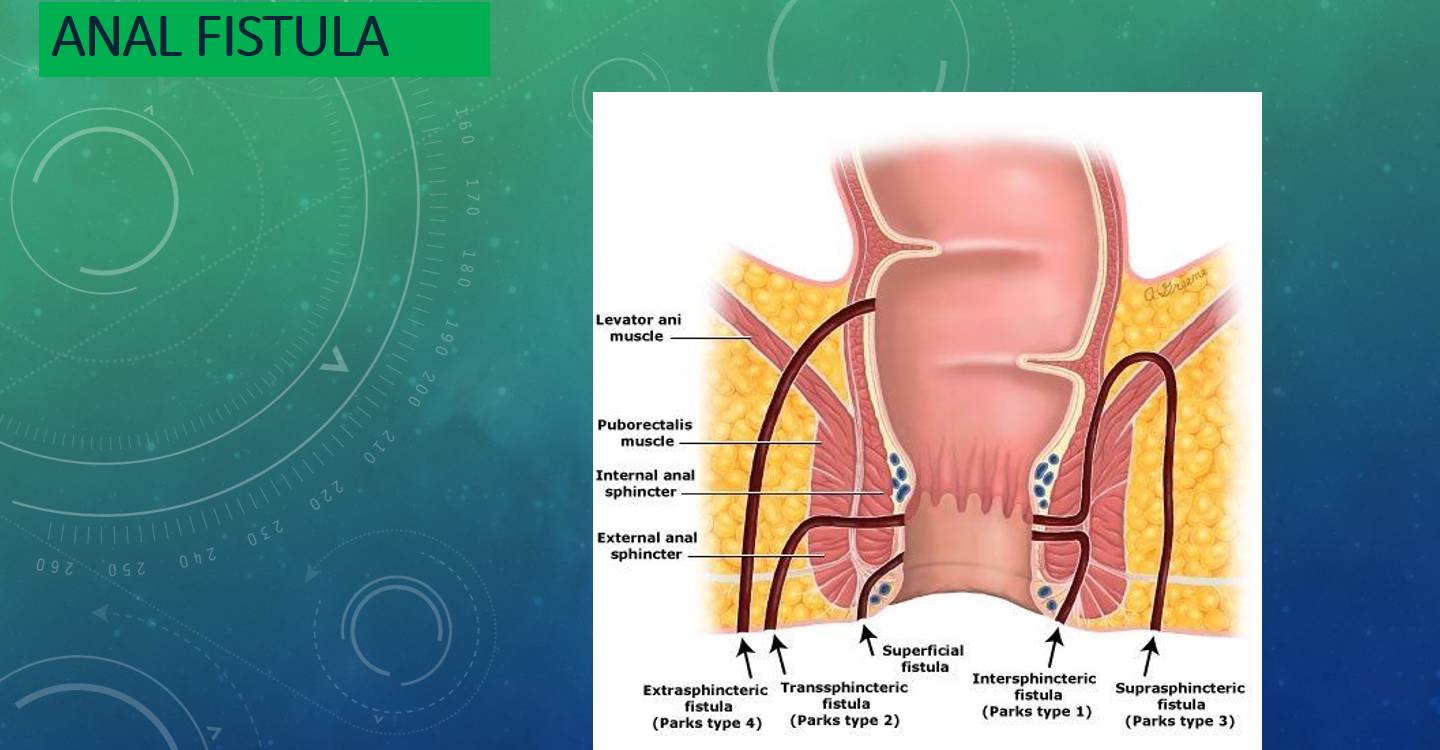
WHAT IS AN ANAL FISTULA?
Anal fistula in simple words is a tube or a tract lined by granulation tissue extending from the Anal canal to the skin around the anal opening.
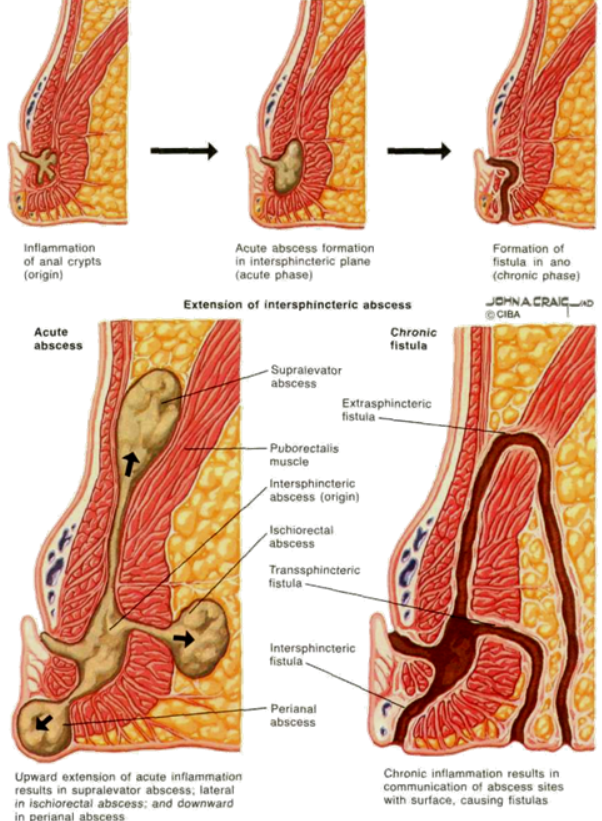
How does an Anal fistula develop?
There are a number of small glands in the wall of anal canal that make mucus which helps in passage of stools during defecation. Due to poor dietery habits and chronic constipation sometimes, these glands get blocked by hard stool particles and can become infected leading into an abscess. When there is delay in surgical drainage of such abscesses or the patient allows it to spontaneously rupture , 40 %-50% of these wounds fail to heal leading to development of fistulas.
Minority of Anal fistulas develop with other disease processes or conditions including Crohn’s disease, radiation, malignancy, trauma , foreign body, previous surgery (including ileoanal pouch surgery), tuberculosis, HIV infection, hidradenitis suppurativa, lymphogranuloma venereum, perianal actinomycosis, and rectal duplication.
SYMPTOMS OF ANAL FISTULA & TYPES OF ANAL FISTULA
In almost all cases there is a previous history of drainage of anal abscess either spontaneously or surgically.
There are 4 types of anal fistulas:
-Intersphincteric fistula where the tract pierces the internal anal sphincter, passes in the space between the internal and external anal sphincter muscles and opens close to the anal opening.
-Transphincteric fistula where the tract passes through the internal and external sphincter muscles and opens usually within few centimetres from the anal opening. These fistulas can go around the anal canal with multiple external openings on both sides of the anus (so called a horseshoe fistula).
-Suprasphincteric fistula where the tract turns upward to a point above the puborectalis muscle and then goes down to open away from the anus.
-Extrasphincteric fistula where the tract usually begins at the recto-sigmoid colon and extends downward to pass through the levator ani muscle and opens around the anus. These fistulas are usually caused by inflammatory bowel disease like Crohn’s disease and can be multiple.
DIAGNOSIS OF ANAL FISTULA
- Most of the fistulas can be diagnosed by digital rectal examination & Proctoscopy by an experienced surgeon or colo- proctologist.
- Proctoscopy some times show the purulent discharging internal opening, which commonly lies at the Dentate line.
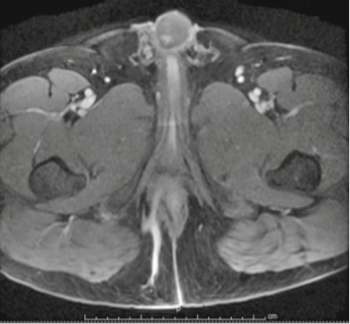
- A MRI fistulogram sometimes is mandatory to delineate the fistula tract type, its relation to the anal sphincters and any branching or deep abscesses. A simple blood test of ‘serum creatinine’ is a must before going for contrast MRI examination.
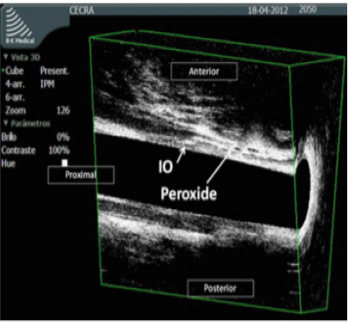
- A hydrogen peroxide enhanced 3D Endorectal Ultrasound is available in few centres which shows the anatomy of fistula tract and its relationship with the anal sphincters. A three dimensional course study of the fistula tract is an added advantage for the operating surgeon.
- Colonoscopy or Flexible Sigmoidoscopy is some times necessary in diagnosis of complex fistula.
MANAGEMENT OF ANAL FISTULA
Goals of Treatment for Anal fistula
-
Control of Infection/Sepsis/Pain
-
Preservation of Function of Anal sphincters
-
Ablation of Fistula tracts resulting in closure
-
Prevention of Recurrence
A number of available procedures for treatment of Anal fistula itself signifies that any one procedure does not fit all the fistula types.
Even with the modern procedures and in expert hands recurrence rate for anal fistula varies from 10 to 20 percent worldwide.
HYDROGEN PEROXIDE ENHANCED 3D ENDORECTAL ULTRASOUND SHOWING FISTULA TRACT
CONTRAST MRI SCAN SHOWING FISTULA TRACT (BLUE ARROW)
PROCEDURES FOR TREATMENT OF ANAL FISTULAS BROADLY FALL INTO TWO GROUPS
1) Sphincter cutting procedures
- Fistulotomy or Lay open techniques
- Fistulectomy & Primary Sphincter Repair
- Cutting Seton
2) Sphincter sparing procedures
- Seton insertion (Draining seton)
- Fibrin sealant
- Endorectal advancement flaps & dermal advancement flap
- Biologic and synthetic fistula plugs
- Ligation of intersphincteric fistula tracts (LIFT)
- Submucous ligation of fistula tract. ( SLOFT )
- VAAFT (Video assisted anal fistula treatment)
- FILAC (fistula laser closure)
- DLPL ( Distal laser & proximal ligation )
LASER is often used in combination with VAAFT, SLOFT, Endorectal advancement flaps to improve outcome.
Intra-operative demonstration of low transphincteric anal fistula
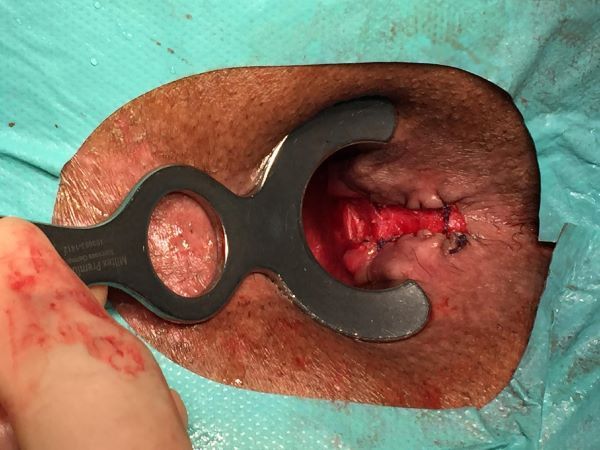
Lay open of the low transphincteric anal fistula With marsupialization
Gentle probing of low transphincteric Anal fistula tract
- Gentle probing is done only by experts in the field to avoid any false passage formation.
- Probing also helps the Specialist to know the size of anal sphincter muscle so as to take a decision regarding the type of surgery which would benefit his patient without causing anal incontinence .
Endorectal advancement flap for anal fistula
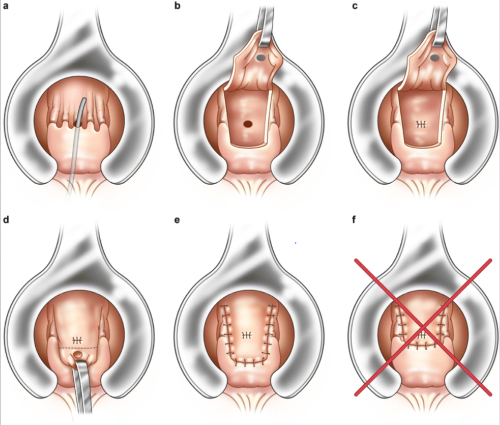
- Success of fistula surgery depends on effective closure of the internal opening after dealing with the fistula tract by other methods.
- A flap of rectal mucosa and part of underlying muscle is raised . The internal opening in the muscle is closed separately .
- The raised vascularized flap is brought down to cover up the internal opening & is sutured to the anoderm without tension.
- Cannot be performed in Crohn’s disease due to unhealthy mucosa.
- Patient has to Avoid smoking to promote wound healing.
- Success rate is variable between 67% to 83%.
LIGATION OF INTERSPHINCTERIC FISTULA TRACT ( LIFT PROCEDURE )
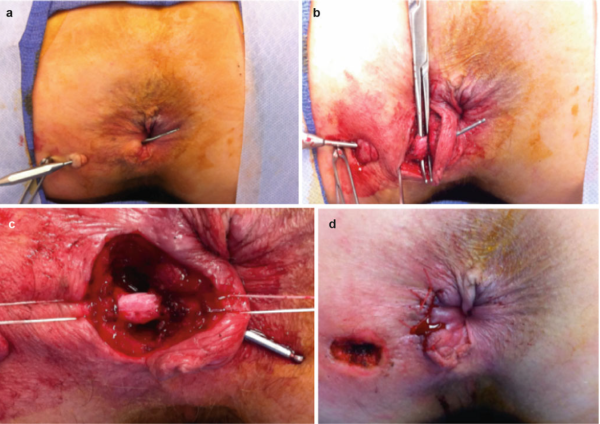
- LIFT is a newer sphincter preserving surgical procedure suitable for transphincteric anal fistulas.
- The fistula tract is exposed via intersphincteric approach .
- Tract is ligated & divided close towards the internal opening.
- The remaining distal tract is either partly excised and closed, or ablated by Laser or curettage. The external opening is excised and widened for drainage.
- Success rate varies from 74% to 90 %.
- LIFT can be effectively offered to patients suffering from Crohn’s fistula as well as to smokers.
VIDEO ASSISTED ANAL FISTULA TREATMENT(VAAFT)
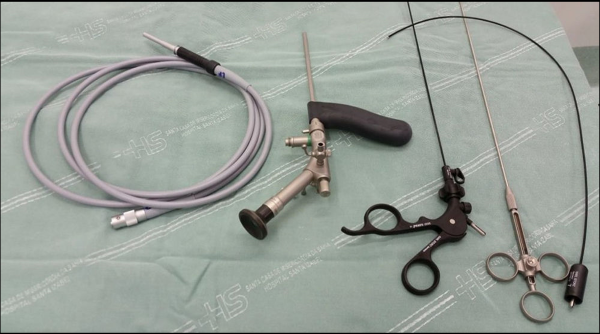
- VAAFT is a novel treatment method for complex anal fistula.
- A tiny rigid video fistuloscope is inserted inside the anal fistula via its external opening. The whole of fistula tract and its side branches if any are visualized on a video monitor.
- The fistula tract is cleaned from inside by a special brush and then the infected granulations are ablated by a monopolar cautery or Laser fibre introduced via instrument channel.
- The internal opening is closed either by special suturing technique or by stapler or by advancement flap.
- Great advantage of this procedure is that the anal sphincter function as well as the anal canal anatomy is well preserved .
- Recurrence rate varies between 15 % - 18%.
LIGATION OF INTERSPHINCTERIC FISTULA TRACT (LIFT PROCEDURE) FISTULA LASER CLOSURE (FILAC PROCEDURE)
- FILAC is a novel procedure aimed at cure of fistula in ano.
- It is a sphincter preserving procedure with minimal post operative discomfort
- Suitable for complex Transphincteric , suprasphincteric , extrasphincteric & intersphincteric fistulas.
- The infected fistula tract is initially drained by inserting a draining seton for few weeks,
- When the infection settles down, Seton is removed and the tract ablated by inserting a Radial 360 Degree laser fibre.
- Internal opening is closed by placing sutures.
- Complete healing occurs in 2 weeks.
- Success rate varies from 84% to 90 %.